Posted by Martijn Grooten on Jun 20, 2017
There are two good reasons not to be concerned about CVE-2012-0158, an RTF handling vulnerability in Microsoft Office. First, the vulnerability was patched more than five years ago, so if you follow good security practices and patch regularly, you won't have to worry about it. Secondly, if you are following those good security practices, you won't be likely to open email attachments sent by strangers: CVE-2012-0158 requires the target to open a document.
Unfortunately, for many users and organizations, patching appears to be more difficult than it might seem from the ivory towers of security bloggers. What's more, malicious emails have long been disguising themselves as emails that explicitly do not come from strangers, thus making the opening of the attached documents a seemingly safe thing to do.
As a result, over the past five years CVE-2012-0158 has been used in APT attacks, in attacks against civil society and, as recently as three months ago, in a large spam campaign.
CVE-2012-0158: powering electronic repression of Chinese dissidents and ethnicities for years. Best #ROI ever.
— Nex ~ Claudio (@botherder) December 19, 2016
But CVE-2012-0158 may have finally found a successor in CVE-2017-0199, another vulnerability in Microsoft Office. The first known exploit of this vulnerability was used in the wild in November last year, and samples exploiting what was still a zero-day vulnerability were written about by security firms in April of this year. A few days later, on 10 April, the exploit was used in a large campaign spreading the Dridex trojan (a rare case of a zero-day exploit being used in the wild on a large scale) before Microsoft released a patch for the vulnerability a day later.
According to Sophos researcher Gabor Szappanos, who has written a paper on CVE-2017-0199, more than three quarters of malicious office documents now use this exploit, with CVE-2012-0158 a very distant second. (Note that this does not include Office documents with malicious macros embedded in them; the only vulnerability these exploit are gullible humans.)
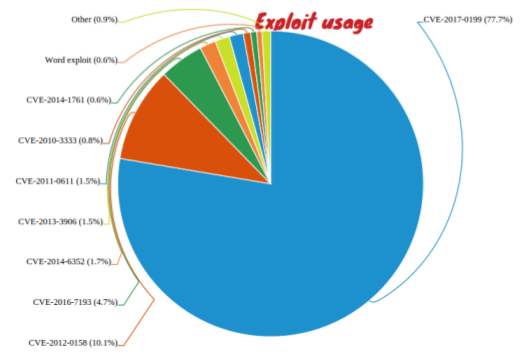
In the paper, Gabor looks at the history of the exploit and how various groups have been using it. He also looks at how it found its way into Office exploit builders, rogue software toolkits that automate the creation of malicious exploits and that are commonly used in both APTs and cybercrminal attacks.
Gabor will present a paper on Office exploit builders at VB2017 in Madrid. He will analyse five such exploit builders, all of which are used to generate actual malware. Perhaps unsurprisingly, the only vulnerability that all five builders 'support' is CVE-2012-0158, which itself was the subject of a VB conference paper in 2013 (pdf). No doubt, by the time Gabor presents his paper in October, CVE-2017-0199 will feature just as prominently, if not more so.
Join Gabor and more than 50 other security experts from around the world for VB2017 in Madrid. Register before the end of June to quality for a 10% Early Bird discount. A number of sponsor opportunities are still available.
